When it comes to heart health, an EKG borderline ECG can signal potential underlying issues that require further investigation. An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a critical diagnostic tool used to assess the electrical activity of the heart. A borderline ECG result may indicate abnormalities that warrant closer attention. Understanding the nuances of an EKG borderline ECG is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals.
An EKG borderline ECG can be concerning for many individuals, especially when they receive their test results. However, it is important to understand that a borderline ECG does not always mean there is a severe underlying condition. In many cases, additional tests and evaluations are necessary to confirm or rule out specific heart conditions.
This article aims to provide a detailed overview of EKG borderline ECG, including its causes, implications, and management strategies. By the end of this guide, you will have a clearer understanding of what it means to have a borderline ECG and the steps you can take to ensure your heart health is properly monitored.
Read also:Lisa Boote The Rising Star Of The Digital Age
Table of Contents
- What is EKG Borderline ECG?
- How Does EKG Work?
- Causes of Borderline ECG
- Symptoms Associated with Borderline ECG
- Diagnosis of Borderline ECG
- Management and Treatment
- Prevention Tips
- Common Myths About EKG
- Importance of Regular Heart Checkups
- Conclusion
What is EKG Borderline ECG?
An EKG borderline ECG refers to an electrocardiogram result that shows minor abnormalities or irregularities but does not clearly indicate a specific heart condition. In some cases, these irregularities may be due to physiological variations or minor issues that do not necessarily pose immediate health risks. However, a borderline ECG result often prompts further investigation to rule out or confirm underlying heart conditions.
Electrocardiograms are essential tools in diagnosing heart conditions, and understanding the implications of a borderline ECG result is crucial. It is important to note that a borderline ECG does not always mean there is a serious problem, but it does highlight the need for additional monitoring or tests.
Some common variations that may result in a borderline ECG include minor changes in heart rhythm, slight deviations in electrical activity patterns, or minor ST-segment and T-wave abnormalities. These variations can be influenced by factors such as age, gender, physical activity, and overall health status.
How Does EKG Work?
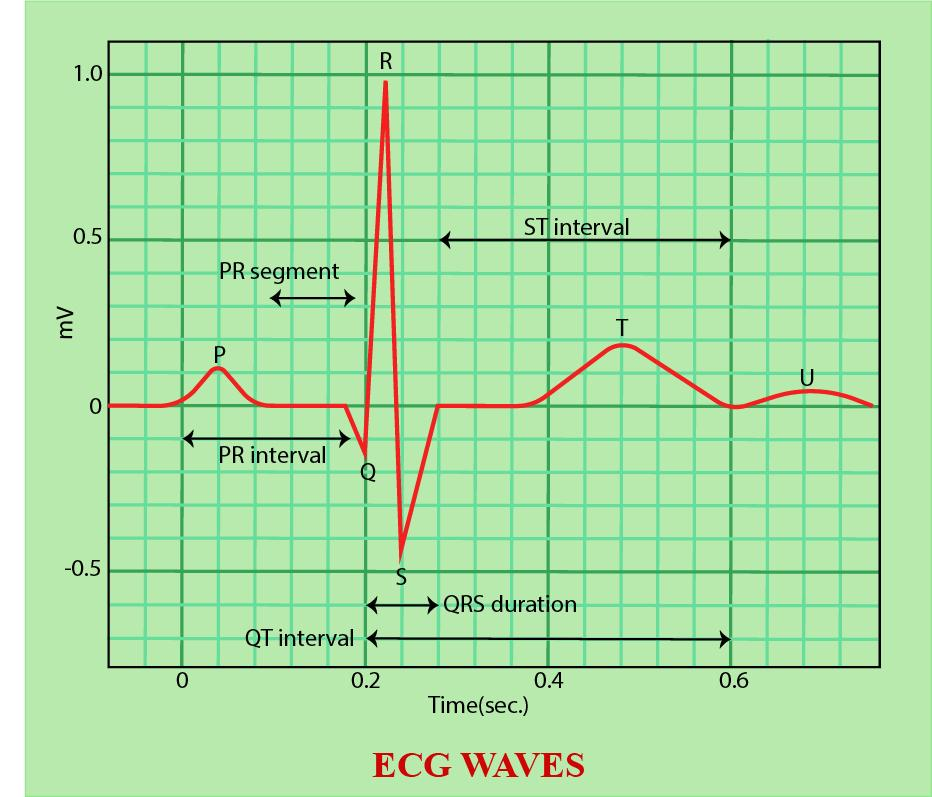
An electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) measures the electrical activity of the heart. It detects the electrical signals generated by the heart during each heartbeat and translates them into a graphical representation known as an ECG tracing. This tracing provides valuable insights into the heart's rhythm, rate, and overall function.
Key Components of an EKG
- Electrodes: Small sensors placed on the skin to detect electrical signals.
- Leads: Wires that connect the electrodes to the EKG machine.
- Tracing: The graphical output showing the heart's electrical activity over time.
The EKG machine records the electrical impulses as waves, which are then analyzed by healthcare professionals to identify any irregularities. These waves include the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave, each representing different phases of the heart's electrical activity.
Read also:Buffstreams The Ultimate Guide To Streaming Sports Online
Causes of Borderline ECG
There are several potential causes of a borderline ECG result. While some factors may be benign, others may indicate underlying heart conditions that require further evaluation. Below are some common causes:
- Physiological Variations: Normal variations in heart rhythm or electrical activity.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Abnormal levels of potassium, calcium, or magnesium can affect heart function.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can lead to changes in the heart's electrical activity.
- Heart Muscle Changes: Conditions such as hypertrophy or fibrosis can alter ECG patterns.
- Medication Effects: Certain medications may influence heart rhythm and electrical activity.
Understanding the underlying cause of a borderline ECG is essential for determining the appropriate course of action. Healthcare providers often consider a patient's medical history, lifestyle factors, and other diagnostic tests when evaluating borderline ECG results.
Symptoms Associated with Borderline ECG
While a borderline ECG does not always cause noticeable symptoms, some individuals may experience mild symptoms that warrant attention. These symptoms may include:
- Mild Chest Discomfort: Occasional discomfort or pressure in the chest area.
- Palpitations: Awareness of the heartbeat or irregular heartbeats.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing during physical activity or rest.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness or lack of energy.
- Dizziness: Occasional lightheadedness or fainting spells.
It is important to note that these symptoms can be associated with various conditions and may not necessarily indicate a serious heart problem. However, if you experience any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Diagnosis of Borderline ECG
Diagnosing the cause of a borderline ECG typically involves a combination of tests and evaluations. Below are some common diagnostic approaches:
- Repeat ECG: Conducting another ECG to confirm or rule out abnormalities.
- Exercise Stress Test: Monitoring heart activity during physical exertion.
- Echocardiogram: Using ultrasound to assess heart structure and function.
- Holter Monitor: Recording heart activity over a 24-48 hour period.
- Blood Tests: Checking for markers of heart damage or other conditions.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the appropriate management strategy. Misinterpreting a borderline ECG result can lead to unnecessary anxiety or delayed treatment. Healthcare providers rely on a comprehensive evaluation to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Management and Treatment
The management and treatment of a borderline ECG depend on the underlying cause and the presence of any associated symptoms. Below are some common management strategies:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Medication: Prescribing medications to address specific conditions or symptoms.
- Regular Monitoring: Scheduling follow-up ECGs or other tests to track changes in heart function.
- Cardiac Rehabilitation: Participating in programs designed to improve heart health and overall well-being.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience worsening symptoms or new symptoms such as severe chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting, it is important to seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires urgent evaluation and treatment.
Prevention Tips
Preventing borderline ECG results and maintaining heart health involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits. Below are some prevention tips:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Focus on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in moderate physical activity for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Manage Stress: Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation or yoga.
- Monitor Blood Pressure: Keep blood pressure within a healthy range through lifestyle changes or medication.
- Avoid Smoking: Quit smoking and avoid exposure to secondhand smoke.
By incorporating these prevention strategies into your daily routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart conditions and improve your overall cardiovascular health.
Common Myths About EKG
There are several myths surrounding EKGs and borderline ECG results. Below are some common myths debunked:
- Myth: A borderline ECG always indicates a serious heart condition.
- Fact: Many borderline ECG results are benign and do not require immediate intervention.
- Myth: EKGs can diagnose all heart conditions.
- Fact: EKGs are just one tool in diagnosing heart conditions and often require additional tests for a complete evaluation.
- Myth: Only older adults need EKGs.
- Fact: EKGs can be beneficial for individuals of all ages, especially those with risk factors for heart disease.
Understanding these myths and facts can help alleviate unnecessary anxiety and promote informed decision-making regarding heart health.
Importance of Regular Heart Checkups
Regular heart checkups are essential for maintaining cardiovascular health and detecting potential issues early. Early detection and management of heart conditions can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications. Below are some reasons why regular heart checkups are important:
- Identifying Risk Factors: Detecting and addressing risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Monitoring Changes: Tracking changes in heart function and electrical activity over time.
- Preventing Complications: Implementing preventive measures to reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other complications.
How Often Should You Get a Heart Checkup?
The frequency of heart checkups depends on individual risk factors and medical history. In general, adults should have a heart checkup every 1-2 years, while those with known risk factors or existing conditions may require more frequent evaluations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding EKG borderline ECG is crucial for maintaining heart health and addressing potential concerns. While a borderline ECG result may indicate minor abnormalities, it does not always mean there is a serious underlying condition. By working closely with healthcare providers and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can effectively manage their heart health and reduce the risk of complications.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information and to leave a comment below if you have any questions or insights. For more in-depth information on heart health and related topics, explore our other articles on the website.